Visual recognition of social signals by a tectothalamic neural circuit
authors: Johannes M. Kappel, Dominique Förster, Katja Slangewal, Inbal Shainer, Fabian Svara, Joseph C. Donovan, Shachar Sherman, Michał Januszewski, Herwig Baier, Johannes Larsch
doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04925-5
CITATION
Kappel, J. M., Förster, D., Slangewal, K., Shainer, I., Svara, F., Donovan, J. C., Sherman, S., Januszewski, M., Baier, H., & Larsch, J. (2022). Visual recognition of social signals by a tectothalamic neural circuit. Nature, 608(7921), 146–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04925-5
ABSTRACT
Social affiliation emerges from individual-level behavioural rules that are driven by conspecific signals. Long-distance attraction and short-distance repulsion, for example, are rules that jointly set a preferred interanimal distance in swarms. However, little is known about their perceptual mechanisms and executive neural circuits. Here we trace the neuronal response to self-like biological motion, a visual trigger for affiliation in developing zebrafish. Unbiased activity mapping and targeted volumetric two-photon calcium imaging revealed 21 activity hotspots distributed throughout the brain as well as clustered biological-motion-tuned neurons in a multimodal, socially activated nucleus of the dorsal thalamus. Individual dorsal thalamus neurons encode local acceleration of visual stimuli mimicking typical fish kinetics but are insensitive to global or continuous motion. Electron microscopic reconstruction of dorsal thalamus neurons revealed synaptic input from the optic tectum and projections into hypothalamic areas with conserved social function. Ablation of the optic tectum or dorsal thalamus selectively disrupted social attraction without affecting short-distance repulsion. This tectothalamic pathway thus serves visual recognition of conspecifics, and dissociates neuronal control of attraction from repulsion during social affiliation, revealing a circuit underpinning collective behaviour.
fleeting notes
-
social affiliation driven by conspecific signals
-
long distance attraction
-
short distance repulsion
-
self like biological motion - visual trigger for affiliation
-
tectothalamic pathway - visual recognition of conspecifics - circuit for collective behavior
-
animals live in groups and require detection of conspecifics
- social affiliation - prerequisite of consummatory actions like aggression and mating. also helps form swarms and flocks
-
goal of paper is to find visual circuits that direct social behaviors
-
used unbiased maps of neural activity after shoaling through rapid fixation and labeling of c-fos with in situ hybridization
- found 31 distinct clusters
- different areas of the brain were activated depending on the visual stimulus - (virtual continuous moving dot, biological movement virtual, and conspecific)
-
volumetric 2p imaging
- response to virtual conspecific most prominent in TeO
-
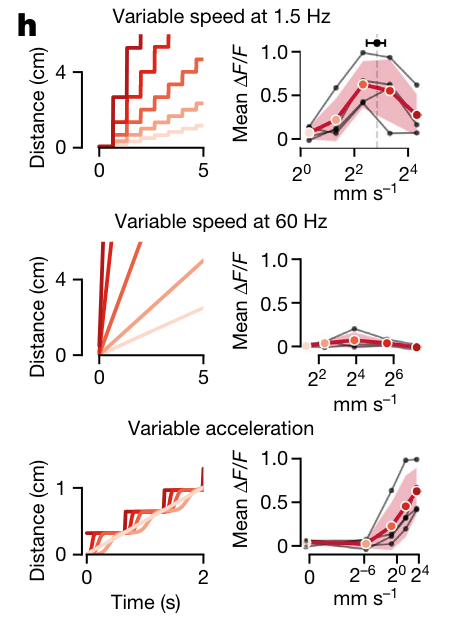
bout preference index = normalized difference in response to the bout like motion vs unattractive motion
-
dorsal thalamic neurons in zebrafish are specifically tuned to conspecific fish-like motion
-
social behaviors in fish depend on specifically tuned visual circuits
-
Dorsal Thalamus has the highest density of bout preference neurons
- detect biological motion
- peak response at naturalistic swim bout frequency
- no response to continuous speed
- DT-BPNs are tuned to detection of fish movement during shoaling
- they do not detect self motion induced visual signals
-
development of DT-BPN is independent from social experience
-
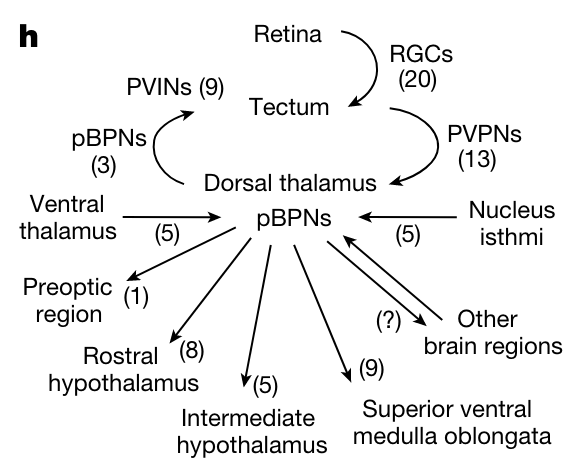
input to DT neurons come from PVPNs which receive input from retinal ganglion cells
- then output is to brain regions proposed to regulate social behavior
-
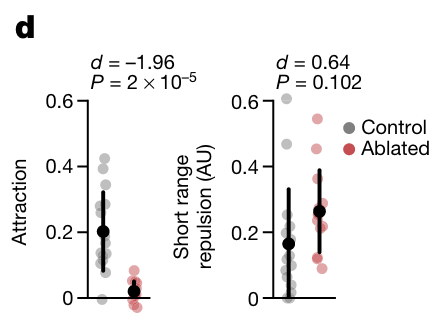
social attraction and shoaling behaviors require visual motion detection circuits
- ablated BPNs and saw decrease in shoaling behaviors but no effect on swimming or other visually evoked behaviors like looming, object avoidance, etc