activation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) gated cation channels is required for thermosensation in all nematodes. the channels are composed of subunits of the tax-2 and tax-4 genes. these genes are the genetic markers of AFD neurons (AFD neurons are required for positive thermotaxis)
It is still unclear to me the biophysics of how this receptor confers temperature sensitivity. Are these analogous to TRP channels? Do they have the same action?
- Takeishi et al 2016 suggests yes to these questions in c elegans… still unclear what the mechanism is to me though in the initial temperature sensing step. See diagram below for proposed pathway (from Bryant.etal2022):
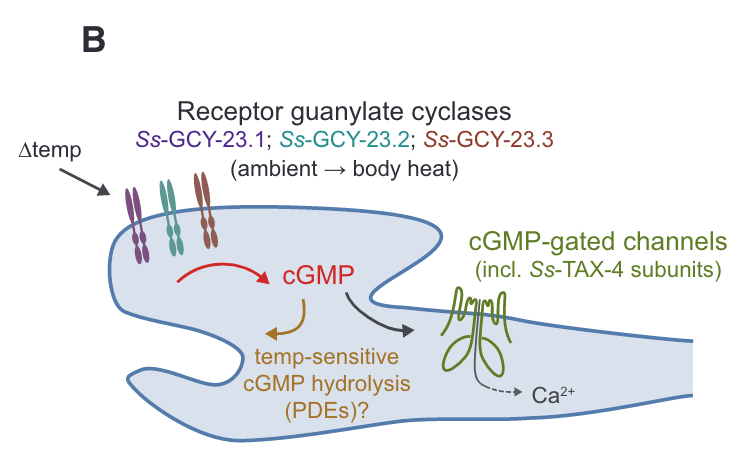
rGCs are the thermosensors themselves in s stercoralis as well (Bryant.etal2022 Fig 6).
rGCs are also used for chemotaxis behaviors in c elegans (and most likely strongyloides as well just hasnt been tested)
references
Takeishi, A., Yu, Y. V., Hapiak, V. M., Bell, H. W., O’Leary, T., & Sengupta, P. (2016). Receptor-type Guanylyl Cyclases Confer Thermosensory Responses in C. elegans. Neuron, 90(2), 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.03.002