one of the joys of using flies is the extensive and specific genetic access we have. however, there are some caveats to the tools we use. attP sites were introduced into the genome through P-element transformations. these attP sites enable site directed insertion of transgenes to known locations.
important :
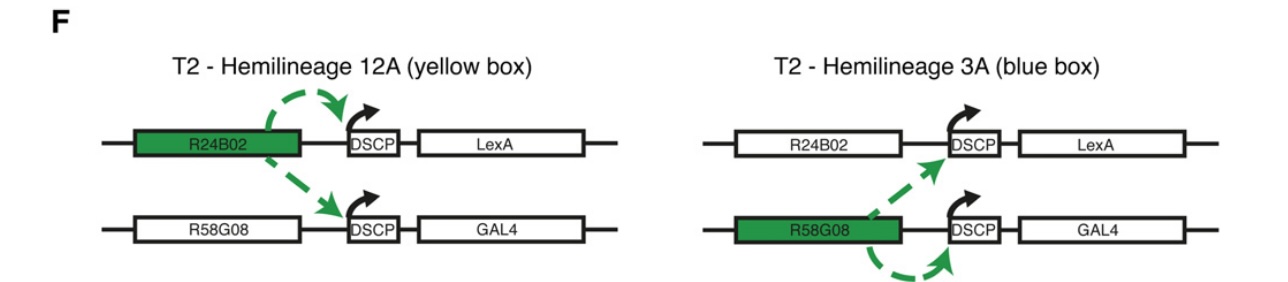
when using intersectional approaches with two different binary expression systems (Gal4 & LexA) together in the fly, transvection requires deliberate consideration! If your LexA and Gal4 drivers are integrated at the same attP site, the promotors may be used to drive trans expression of the opposite transcription factor (x-Gal4 may become x-LexA and y-LexA may become y-Gal4)
fig2F
schematic depicting transvection between transgenes when at the same attP site
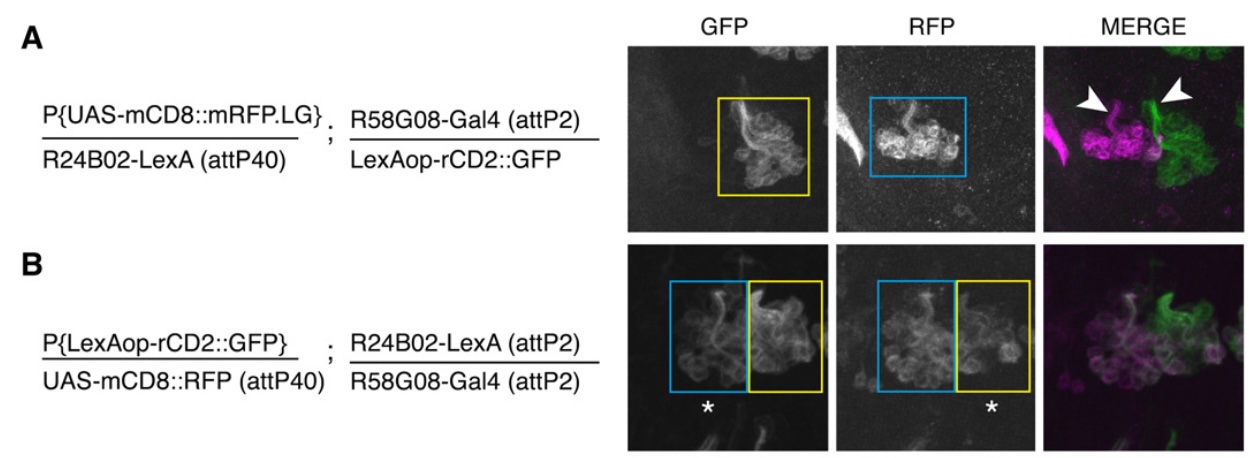
fig2a,b
a) is the control. only one group of neurons is labeled by each reporter (GFP vs RFP) because different attp sites were used for the drivers
b) the result of transvection. you get expression of both neuron groups by each reporter