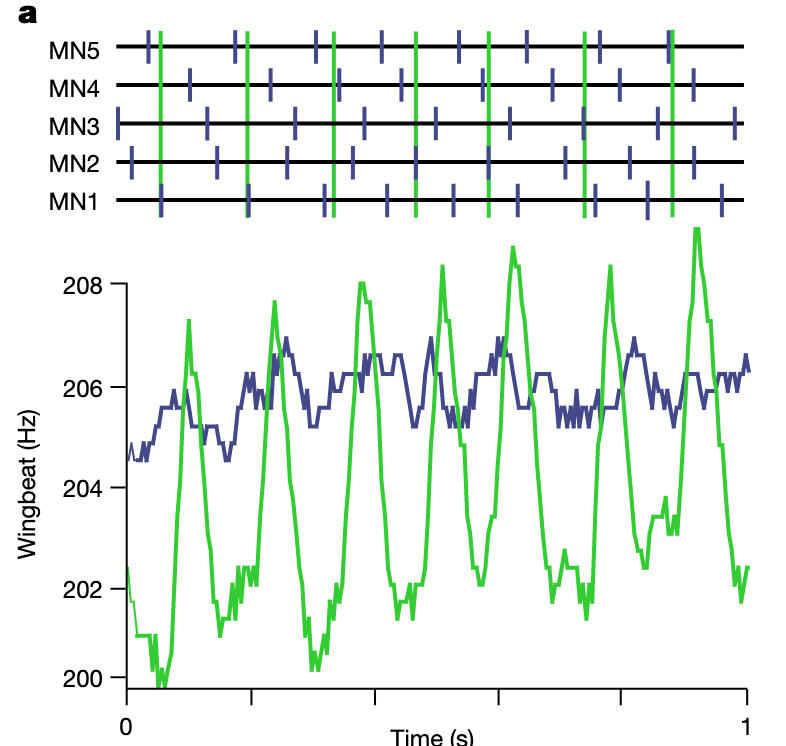
each MN spike causes an increase in calcium in the muscle fiber (DLMns adjust myoplasmic calcium levels to control wing power) and weak electrical coupling between DLMns favors splayed firing pattern.
the splayed firing of MNs establishes a relatively stable calcium level in the muscle. This plot is showing the myoplasmic calcium levels produced by firing of each MN.
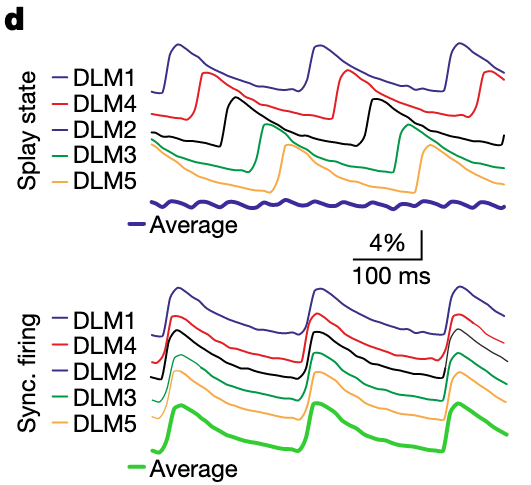
compared to the synchronized motor neurons firing: BIG fluctuations in the average calcium at the muscle.
These can be visualized as readouts of the wingbeat frequency showing stable (splayed state) or big fluctuations (synchronized)